Post Tensioning
SPAN TO DEPTH RATIO
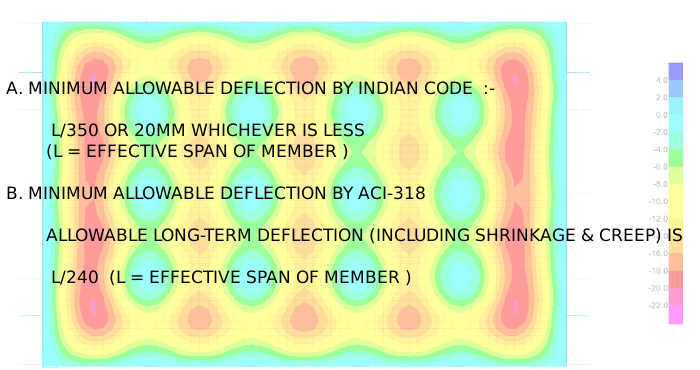
DEFLECTION
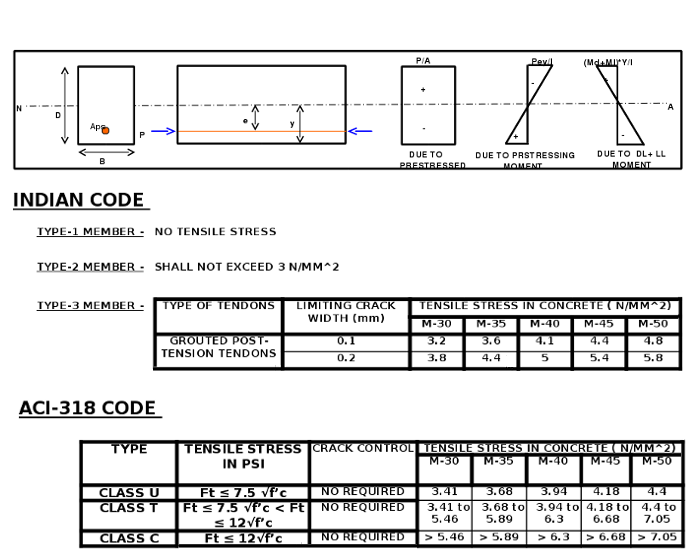
TENSILE STRESS IN CONCRETE
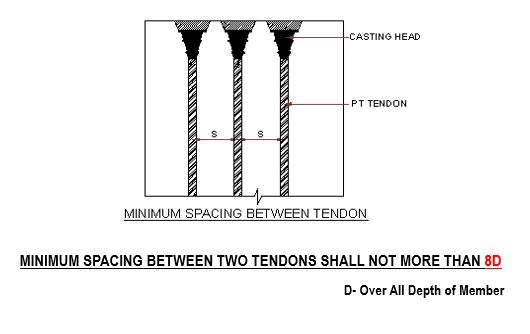
SPACING CRITERIA FOR PT TENDONS
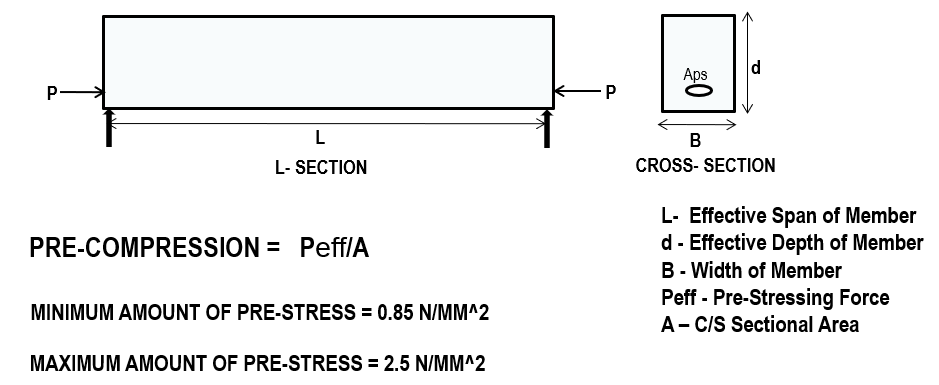
AMOUNT OF PRE-STRESS
Need For Post-Tensioning
Post-Tensioning offers great technical advantage in comparison to other conventional forms of construction, such as reinforced concrete and steel. Post-Tensioning members possess improved resistance to shearing forces, due to the effect of compressive stress in concrete.
Taking the advantage of the Post-Tensioning Technique following benefits can be achieved —
1
Increase in Flexibility to locate columns at long spans.
2
Decrease in deflection and cracking for PT element.
3
Decrease in dead weight, resulting in reduction of design loads and cost of foundation.
4
More feasibility to have beamless slabs i.e. flat slab with drop.
5
Higher utilization of the floor, making of subdivision of floors easy.
6
Lesser de-shuttering time and speedy construction.
7
Reducing concrete consumption, due to thinner section.
8
Huge reduction in steel quantity and therefore cost of construction.
9
Building height lesser than conventional.
What is Bonded Post - TensioningTechnique
Prestressed concrete is basically concrete in which internal stresses of a suitable magnitude and distribution are introduced so that the stresses resulting from external loads are counteracted to a desired degree.
“Post-Tensioning is system which generates the compressive stress in the harden concrete using the HT-Strands”
In Bonded Systems- two or more HT strands are inserted into a metallic duct that is embedded in the concrete. The HTstrands are tensioned with the help of Hydraulic Jacks and anchored in anchorage devices. The duct is then filled with the cementious grout that protects the HT strands from corrosion and bonds the HT strands to the concrete surrounding the duct.
Bonded systems are commonly used in bridges, super and sub-structure of buildings and transfers girders. In this system large number of strand can be used to achieve the economical PT options.
How does compressive stress occur?
The Tendons are laid out in forms in accordance with installation drawings that indicate how they are to be spaced, what their profile should be. After concrete is placed and has achieved the compressive strength min 25N/mm2, the tendons are stressed and anchored.
The Tendons, like rubber bands, tends to return to their original length but they are prevented from doing so by anchorages. The fact that tendons are kept in permanently stressed (elongated) state causes a compressive force on concrete.